Find out about improvisation and different styles of music.
Learn about how Snarky Puppy, Herbie Hancock and Miles Davis use improvisation in their music.
Have a go at improvising your own piece of music.
Watch how the band use their instruments to improvise together.
SAXOPHONE PLAYING
Ben: Okay, guys. Let’s take it from the bridge. We’ll keep the beat going and we’ll improvise with our instruments over the top of the bridge chords. Take it in turns and just see which one we like best.
Dujon: One, two, three-
MUSIC
PIANO SOLO
MUSIC CONTINUES
GUITAR SOLO
DRUM SOLO
SAXOPHONE SOLO
Improvisation is another word for being able to create music on the spot. This is a way of responding to other people playing in a group and usually reflects the style of music that is being performed.Often a performer will improvise around the melodies that appear in a song or a piece of music, perhaps expanding or varying them slightly.
New musical ideas are created when performers improvise with their instruments. Sometimes the chord progressions that form the foundation of a song might be changed, so an improvisation might include reharmonisations - different chords harmonising the same melody.

Just like vocal improvisation, instrumental improvisation comes in different shapes and sizes depending on the musical style. Here are a few examples:
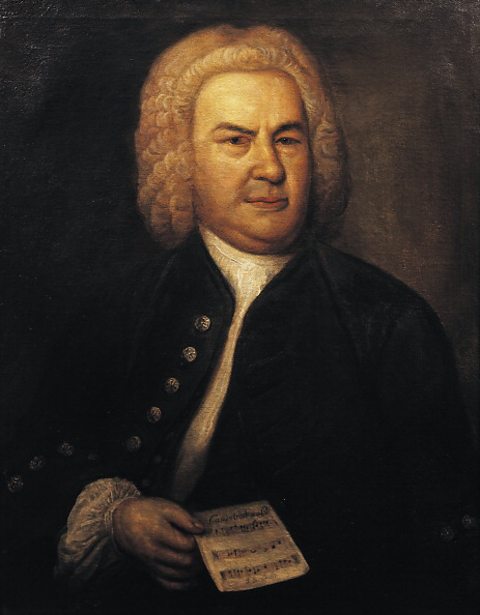
Baroque period (1600-1750)
Many of Johann Sebastian Bach’s keyboard and organ compositions started off as improvisations. In the pieces, there is often room for the performer to add their own ornaments or decorations to the music. The musicians would add extra notes and techniques to make the melody lines more elaborate.
Classical period (1750- circa 1810)
Concertos were pieces of music for a soloist and orchestra which often featured a cadenza. A cadenza is a short section in which the solo instrumentalist would improvise without the orchestra to show their technical skill.
Present day - Jazz
Perhaps the most popular genre for improvisation is jazz. Jazz covers a breadth of styles, involving improvising for all instruments as well as vocalists.

Listen to these examples of improvising with instruments
In Watermelon Man by Herbie Hancock, the trumpet improvises over the chord progression and plays a similar shape to the original melody, but decorates it by adding extra notes.
This is Lingus by Snarky Puppy. Cory Henry plays this notable solo from the last decade, featuring lots of fast scalic passages - where a player creates a melody by going up and down a scale on their instrument.
In So What by the Miles Davis Quintet, the trumpet player and band leader Miles Davis hands over the improvising to John Coltrane, who plays the tenor saxophone.
Improvise your own tune
Improvising is a great instrumental skill to have, but it can require some hard work at the beginning. When you are starting out, the first thing to remember is that you shouldn’t worry about making any mistakes - some improvisations will sound a little more ‘musical’ than others. Play a few notes on an instrument of your choice and take it from there - you don’t need to be an expert.
One of the best ways into improvisation is the 12-bar blues. This is a well-known, simple chord progression which gives you an opportunity to try out some of your ideas.
Listen to the 12-bar blues backing track and try singing or playing over the top of it using the notes of the C major blues scale.
If you’re unsure of where to begin, start by improvising with two or three notes - for example the bottom three (C, E♭ and F) or even the top three (G, B♭ and C). Finish your improvisation on a C or a G as these are the dominant notes of the scale, so they will make the improvisation feel complete.
Once you are more confident, you can improvise using more notes from the blues scale.
Watch the video to listen to all the notes in a C major blues scale.
Keywords
| Keyword | Definition |
|---|---|
| improvisation | The art of making up music on the spot or in the moment. |
| melody | The main tune in any piece of music. |
| chord progression | A sequence of chords played in a certain order. |
| reharmonisation | When the existing chord progression of a melody is changed and different chords are used to harmonise the same melody. |
| ornamentation | When melodies are decorated, often with trills or mordents, or sometimes simply with passing notes. |
| decoration | Where an existing melody has notes added to it, or the shape of the melody is changed. |
| 12-bar blues | A well known chord progression of 12 bars using the primary chords. |
| blues scale | A scale which is often the basis for improvisation, especially in the 12-bar blues. |
GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Performing music
Find out more by working through a topic
- count4 of 6

- count5 of 6
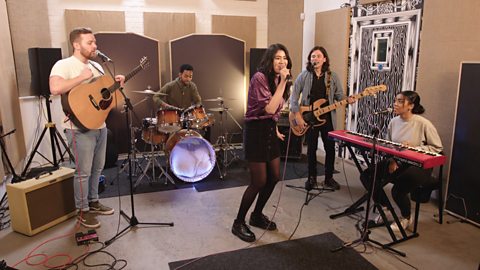
- count6 of 6

- count1 of 6
