Welcome to The Regenerators.
Introduction
From the smallest snowdrops to the tallest oaks, it all begins with a seed.
Plants everywhere, of every shape and size, share a similar life cycle.
They all grow, change and reproduce throughout their life.
What is a seed?
A seed is like a tiny parcel containing everything a new plant needs to start growing.
It contains the young plant (embryo) and store of food. This is all wrapped up in a tough, protective coat.
For a seed to start growing, it needs the right conditions. These can be different depending on the plant; however, for most plants, it’s moisture from the soil, oxygen and the right temperature.
When a seed has found the right conditions it breaks open and it sends out a root and a green shoot. This is calledgerminateWhen a seed begins to develop into a new young plant..
The root grows down to take up nutrients from the soil and the shoot grows up towards the sunlight to become a stem. The seed becomes a seedling.
As this happens the plant is using the food store in the seed to grow, but as leaves begin to form, the plant can start making its own food in a process called photosynthesisThe process in which plants use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to create their own food and oxygen..
Growth
Plants grow to different sizes and at different rates. Plants need these important requirements to grow.
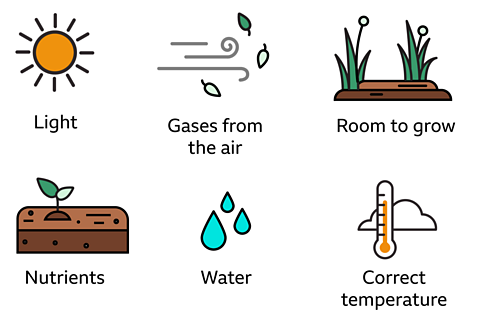
Some plants only grow for a season. These plants are known as annuals.
Other plants, known as biennials, grow in the first year, then produce flowers and seeds in the second year.
Perennials return season after season. Their roots lie dormant during winter, but jump back into life again each Spring.
Trees and shrubs keep growing for years. In their lifetime they can provide a home and food for thousands of animals.

Flowers
When a plant is fully grown it is ready to reproduce. To do this, some plants produce flowers.
Flowers perform an incredibly important role in a plant's life cycle.
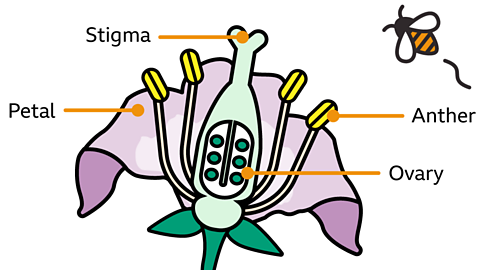
In order to reproduce, pollen from one flower must be transferred to another. This process is called pollinationThe transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant..
Most plants rely on insects and other creatures to carry pollen between flowers.
These plants usually have brightly coloured petals, a strong-smelling scent or a sweet nectar treat. This attracts animals like bees, butterflies, and even birds and bats. Their pollen is usually sticky to attach to these visiting animals.

Other plants use the wind to carry their pollen. As these plants don’t need to attract creatures to pollinate them, their flowers are often small and a dull green or brown colour.

Seed dispersal
After the plant has been pollinated a new seed will start to develop inside the ovary.At this point the flower usually begins to die, the petals fall off leaving behind a fruit with the seeds inside.
For seeds to have the best chance of growing, they need to be transported away from the plant that produced them. Otherwise they would be in competition with each other for light, water and nutrients.
Have a look at some different ways that plants disperse their seeds.

Image caption, Falling
Some seeds, like conkers from horse chestnut trees, just fall to the ground due to gravity. They are often quite heavy and might bounce or roll away from their parent plant.

Image caption, Wind
Other seeds are transported by the wind or a breeze. They are shaped to float or glide through the air with lightweight parts, wings or parachutes.

Image caption, Eaten by animals
Some plants, like this bramble, produce tasty fruits to enclose their seeds. These attract animals to eat them. The seeds can’t be digested, so the seeds pass through the animal’s digestive system undamaged.

Image caption, Carried by animals
Other plants produce fruits which hitch a ride on the fur of passing animals. If you look closely at the seed heads of this burdock, you can see some tiny hooks which make them really sticky.

Image caption, Bursting
Gorse seed pods dry out and crack open on hot summer days, firing the seeds out into the environment.

Image caption, Water
Some plants use water to disperse their seeds. Coconuts can travel hundreds of miles on ocean currents from their parent plants.

Image caption, Fire
Fire might be the last thing you expect to be helpful for a plant. But this plant called Banksia, found in Australia, has woody seed pods which only open after they come into contact with fire.
1 of 7
If everything goes well, a seed will find its own patch of soil with plenty of light and moisture.
From here it will be able to grow and the life cycle will begin again.
Teachers: Sign up for your free seed balls!
To help teach the next generation about the importance of biodiversity, we're teaming up with the BBC One series The Green Planet to give away up to 1 million seed balls to schools across the UK!
The seed balls - called Green Planets, of course - contain a whole world of wildflowers that will help to establish healthy habitats wherever they’re planted, whether that’s the end of a garden or a balcony window box.
Teachers, click below to find out how you can order a pack for your class.
If you're a student, you can ask your parent or carer to send a link to your teacher.
Who knows, maybe you can inspire the nation’s next Sir David Attenborough.
Happy growing!
Lesson complete!
Well done Regenerator, you've completed this lesson. Now let's see what you can remember.
There's more to learn
Explore more lessons and content from around the BBC.
Why are bees so important?
GREEN CLASSROOM

How to look for wildlife in your local space
GREEN CLASSROOM

Year 3 - 6 and P4 - P7
GREEN CLASSROOM

More from The Regenerators
BBC BITESIZE

