Key points about fractions

- A fraction is one way of showing parts of a whole.
- When fractions have the same denominatorNumber written on the bottom of a fraction. The denominator is the number of equal parts, eg for ⅓, the denominator is 3., they can easily be put in size order.
- Every fraction has an infiniteUnlimited, goes on forever without end. Unable to be counted. An endless number. number of equivalent fractionA fraction with the same value as another. Each fraction represents the same proportion, eg ½ and ¹⁰⁄₂₀. .
Support your understanding of this topic with these guides on simplifying fractions and writing equivalent fractions.
Check your understanding
How to simplify fractions and work out equivalent fractions
Follow the examples and working out below.
To simplify (a fraction)To reduce a fraction to its simplest form, also known as its lowest terms. a fraction to its lowest terms, divide the numeratorNumber written at the top of a fraction. The numerator is the number of parts used, eg for ⅓, the numerator is 1. and denominatorNumber written on the bottom of a fraction. The denominator is the number of equal parts, eg for ⅓, the denominator is 3. :
- by their Highest Common Factor (HCF)The greatest factor that will divide into the selected numbers. 10 is the highest common factor of 30 and 20.
or
- by common factorA whole number which is a factor of two or more numbers. 2, 5 and 10 are common factors of 30 and 20. until their only common factor is 1.
To write an equivalent fractionA fraction with the same value as another. Each fraction represents the same proportion, eg ½ and ¹⁰⁄₂₀. :
- multiply the numerator and the denominator by the same number
or
- divide the numerator and denominator by a common factor.
GCSE exam-style questions
- Which of the fractions are equivalent to \(\frac{12}{20}\) ?
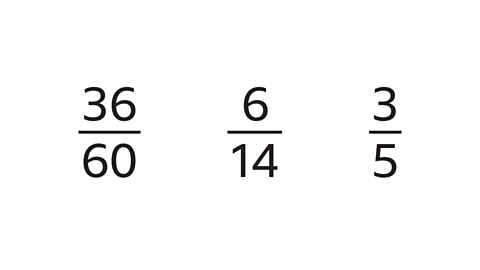
\(\frac{36}{60}\) and \(\frac{3}{5}\) are equivalent to \(\frac{12}{20}\) .
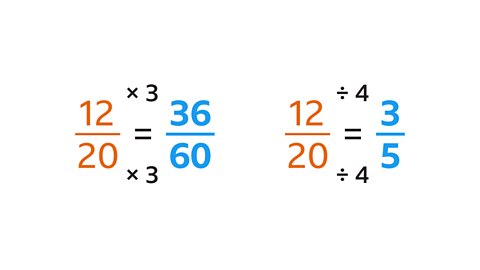
An equivalent fraction is the result of multiplying or dividing the numerator and the denominator of a fraction by the same amount.
- Multiplying the numerator (12) and the denominator (20) by 3 gives the fraction \(\frac{36}{60}\).
- Dividing the numerator (12) and the denominator (20) by 4 gives the fraction \(\frac{3}{5}\).
- Which fraction is \(\frac{15}{40}\) in its simplest form?
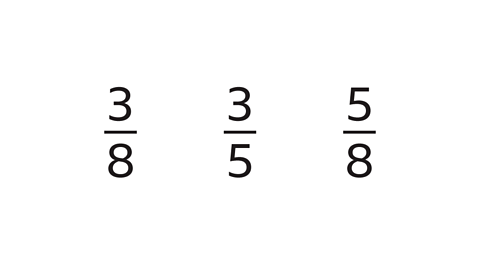
\(\frac{15}{40}\) in its simplest form is \(\frac{3}{8}\).
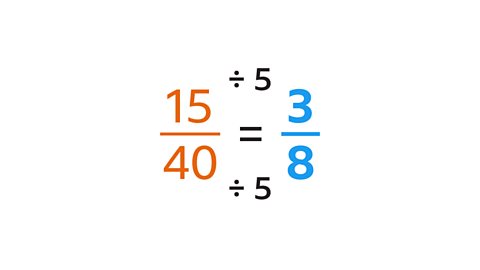
Divide the numerator (15) and the denominator (40) by the HCF of 15 and 40 (5).
15 ÷ 5 = 3 and 40 ÷ 5 = 8.
How to express one quantity as a fraction of another
To express one quantity as a fraction of another, write a fraction and simplify (a fraction)To reduce a fraction to its simplest form, also known as its lowest terms..
The fraction may be less than or greater than one.
Follow the examples and working out below.
For numerical values:
- The first value is the numeratorNumber written at the top of a fraction. The numerator is the number of parts used, eg for ⅓, the numerator is 1., the second value is the denominatorNumber written on the bottom of a fraction. The denominator is the number of equal parts, eg for ⅓, the denominator is 3..
- If possible, simplify the fraction by dividing by common factorA whole number which is a factor of two or more numbers. 2, 5 and 10 are common factors of 30 and 20. .
For quantities given as measures (eg length, area, volume):
- If the quantities are measured in different units, convert one quantity so that both quantities are in the same (smaller) units, eg for minutes and hours express both quantities in minutes.
- Matching units are ignored, and the numerical values are used.
- The first value is the numerator, the second value is the denominator.
- If possible, simplify the fraction by dividing by common factors.
GCSE exam-style questions
- Write 54 cm² as a fraction of 60 cm².
54 as a fraction of 60 is \(\frac{9}{10}\).

The units match, so use the numerical values.
- The first value (54) is the numerator.
- The second value (60) is the denominator.
- Simplify \(\frac{54}{60}\) by dividing by the highest common factor of 54 and 60 (6). Alternatively, simplify by dividing by smaller common factors.
- Write 1250 metres as a fraction of 3 kilometres.
1250 m as a fraction of 3 km is \(\frac{5}{12}\).

The units do not match. Express both quantities in the same (smaller) units (metres)
3 km is 3000 m (3 × 1000 = 3000).
Use the numerical values, 1250 and 3000.
The first value (1250) is the numerator and the second value (3000) is the denominator, so this fraction can be simplified.
How to compare and order fractions
Follow the examples and working out below.
To compare and order fractions:
- Write equivalent fractionA fraction with the same value as another. Each fraction represents the same proportion, eg ½ and ¹⁰⁄₂₀. with a common denominatorNumber written on the bottom of a fraction. The denominator is the number of equal parts, eg for ⅓, the denominator is 3..
- The denominator is the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM)The lowest multiple that is common to two or more numbers. The LCM of 15 and 12 is 60 because it is the lowest value in both of their multiplication tables. Also known as the Least Common Multiple. of the denominators of the fractions.
- Write the fractions in ascending or descending order.
- For a pair of fractions use an inequality symbols (< >)The symbol > is used when a value is greater than another, eg 23 > 5. The symbol < is used when a value is less than another, eg 11 < 40. to show which fraction is greater or less than the other.
Refresh your knowledge on Lowest Common Multiples.
GCSE exam-style questions
- Place an inequality symbol between the fractions to make a true statement.
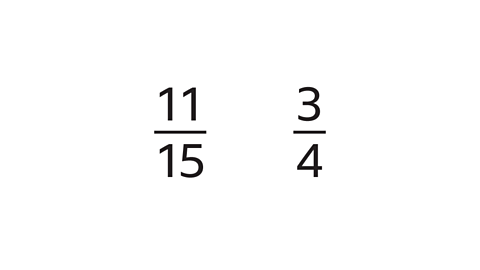
\(\frac{11}{15}\) < \(\frac{3}{4}\)
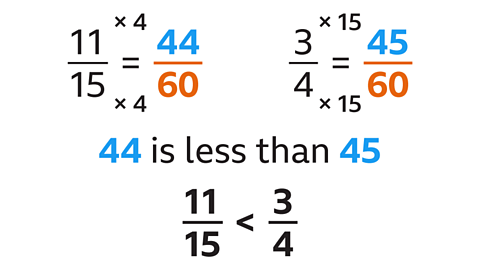
Write the fractions with the same denominator so that they can be compared:
- The LCM of 15 and 4 is 60.
- 44 is less than 45.
- Write these fractions in order of size, starting with the largest.
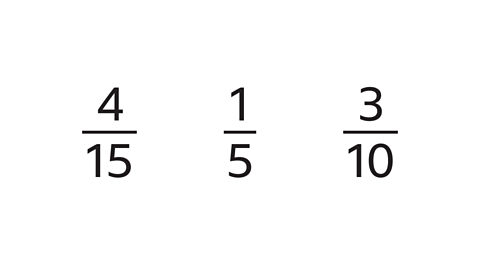
\(\frac{3}{10}\) \(\frac{4}{15}\) \(\frac{1}{5}\)
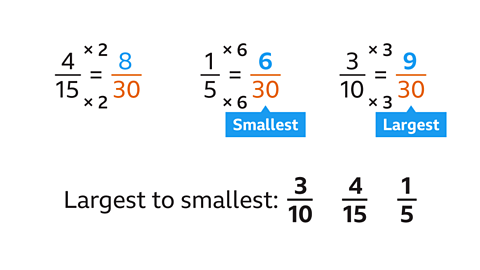
- Write the fractions with the same denominator.
- The LCM of 15, 5 and 10 is 30.
- Turn them into equivalent fractions with a denominator of 30.
- Now compare the numerators.
- The numerators from largest to smallest are 9, 8, 6.
- The fractions can now be ordered from largest to smallest.
Mixed numbers and improper fractions
A mixed number is a whole number and a . It can be converted to an improper fractionA fraction where the numerator is greater than the denominator, eg ⁹⁄₄..
Follow the examples and working out below.
To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominatorNumber written on the bottom of a fraction. The denominator is the number of equal parts, eg for ⅓, the denominator is 3. and add the numeratorNumber written at the top of a fraction. The numerator is the number of parts used, eg for ⅓, the numerator is 1..
- This gives the numerator of the improper fraction.
- The denominator stays the same.
To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number:
- Divide the numerator by the denominator.
- The whole number is the whole number part of the mixed number.
- The remainder is the numerator of the fraction.
- The denominator stays the same.
GCSE exam-style questions
- Convert the mixed number to an improper fraction.
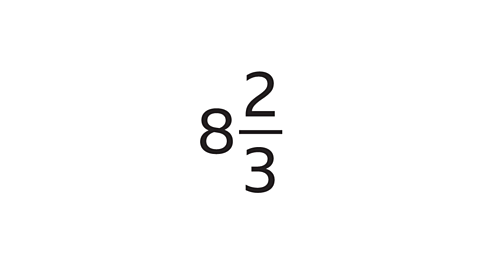
8 \(\frac{2}{3}\)=\(\frac{26}{3}\).
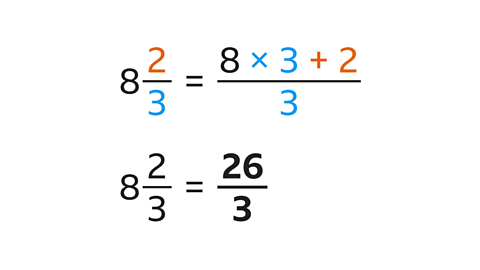
Multiply the whole number (8) by the denominator (3) and add the numerator (2).
- 8 × 3 + 2 = 26.
- The numerator is 26.
- The denominator (3) stays the same.
- Convert the improper fraction to a mixed number.
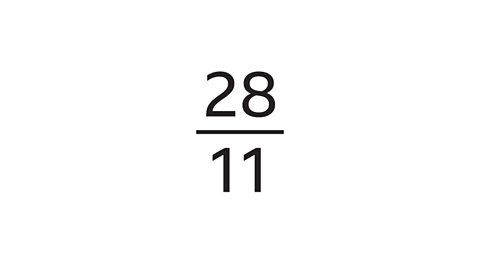
\(\frac{28}{11}\) converts to 2 \(\frac{6}{11}\) as a mixed number.
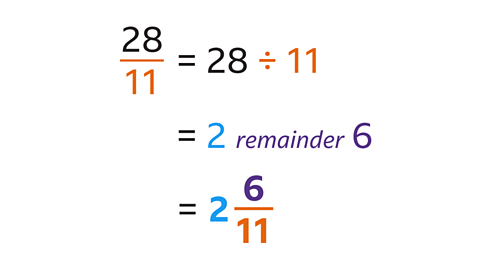
Divide the numerator (28) by the denominator (11).
- 28 ÷ 11 = 2 remainder 6.
- 2 is the whole number part of the mixed number.
- The remainder (6) is the numerator of the fraction.
- The denominator (11) stays the same.
Quiz - Fractions
Practise what you've learned about fractions with this quiz.
Now that you've revised fractions, why not look at fractions, decimals and percentages?
More on Number
Find out more by working through a topic
- count10 of 15

- count12 of 15
