What are the key learning points about prescribed practical C8?
A titration is a practical technique in which an acidCorrosive substance which has a pH lower than 7. Acidity is caused by a high concentration of hydrogen ions. and an alkaliA base which is soluble in water. A base is a substance which neutralises an acid. are reacted together. The volume of one solution needed to neutraliseWhen an acid reacts with a base and this results in the pH of a solution moving towards 7. a set volume of the other solution is carefully measured.
A titration involves the use of a pipetteA piece of apparatus used to measure accurate and repeatable volumes of liquid. and buretteA piece of apparatus used to add varying but measured volumes of solution during a titration. to accurately measure the volumes of the solutions.
An indicatorA chemical that gives a colour change in acidic, alkaline or neutral solutions. must be used to determine the exact volume of solution required for neutralisation.
How to carry out an acid-alkali titration
The process of carrying out a titration allows us to accurately measure the volumes of an acid and an alkali required for neutralisation.
An indicator will be used to determine the exact volume required for neutralisation.
In titration you will attempt to work out the exact volume of sodium hydroxide solution required to neutralise 25 cm3 of sulfuric acid.
In order to carry out this practical you will be using two pieces of volumetric apparatus, the pipette and the burette.
You should aim to carry out the experiment with a high degree of accuracy so the correct volume can be determined.
What apparatus and chemicals are used when carrying out a titration?

Sodium hydroxide solution (100 cm3)
Sulfuric acid (100 cm3)
Phenolphthalein indicator
25.0 cm3 pipette and filler
50.0 cm3 burette, retort stand and burette clamp
Small funnel
250 cm3 conical flask (x3)
Distilled water
White tile
What are the steps involved in carrying out a titration?
Rinse the burette with distilled water, then with the supplied alkali. Fill the burette with the alkali taking care to ensure that the bottom of the meniscusThe curved upper surface of a liquid in a tube. is on zero and that the jet of the burette is filled completely.
Rinse the pipette with distilled water, then with the sulfuric acid. Fill the pipette with the acid, taking care with the pipette filler and ensuring that the bottom of the meniscus is on the ‘line’ of the pipette.
Carefully transfer the acid in the pipette into a conical flask, to remove the final drop from the pipette, gently touch the end of the pipette onto the surface of the liquid in the conical flask.
Add 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator to the conical flask and swirl gently to mix.
Place the conical flask onto a white tile underneath the burette.
Titrate the alkali with the acid, stop adding the alkali when the indicator turns pink and remains pink.
Record your ‘rough’ titre value in the results table.
Repeat the process with fresh acid and indicator, adding the alkali dropwise with swirling as the end point is reached.
Repeat once more, or until 2 titre values are within 0.2 cm3 of each other.
Calculate the average titre.
| Burette volume | Rough | 1st Accurate | 2nd Accurate | 3rd Accurate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial reading / cm3 | ||||
| Final reading / cm3 | ||||
| Titre / cm3 |
Average titre = _________________cm3
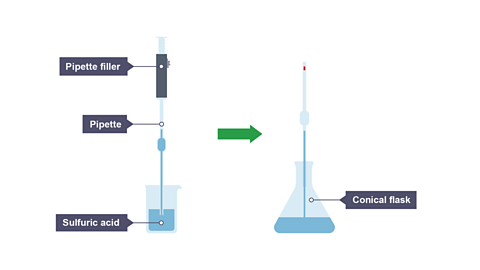
Image caption, Step 1. A pipette and pipette filler is used to transfer 25 cm³ of sulfuric acid into a conical flask.

Image caption, Step 2. A few drops of phenolphthalein is added to the conical flask.
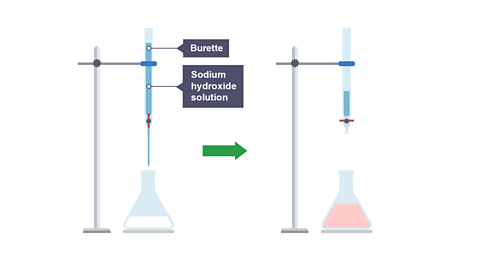
Image caption, Step 3. A burette is used to add sodium hydroxide to the sulfuric acid until the phenolphthalein changes colour to pink. This is the ‘end point,’ and the volume added is recorded as the titre.
1 of 3
To ensure accuracy in a titration:
Read volumes from the bottom of the meniscus.
Add the solution from the burette drop-by-drop near the end point.
Swirl the conical flask during the titration to ensure the solutions are mixed.
To ensure reliability in a titration:
- Carry out at least two accurate titrations and calculate an average titre.
Determine the reacting volumes of solutions of acid and alkali by titration.
How much do you know about prescribed practical C8?
More on Unit 3: Prescribed practicals
Find out more by working through a topic
- count9 of 9

- count2 of 9
