Key facts
Batteries are used to store chemical energy. Placing a battery in a circuit allows this chemical energy to generate electricity which can power device like mobile phones, TV remotes and even cars.
Generally, batteries only store small amounts of energy. More and more mobile devices like tablets, phones and laptops use rechargeable batteries.
Batteries are a non-renewable form of energy but when rechargeable batteries store energy from renewable energy sources they can help reduce our use of fossil fuels and cut down carbon dioxide and greenhouse gas production.

Batteries and their impact
Find out why batteries may have a key role to play in making our energy supply greener.
All batteries are basically stores of chemical energy. Inside a battery, are one or more simple chemical cells. A simple cell must contain an electrolyte and two different metals. It can be made from everyday items like a lemon, zinc nail, and copper penny. The lemon juice in the lemon acts as the electrolyte and the two metals are electrodes. Electricity flows between the two metal. By using different metals you can even produce different voltages.
In a commercial battery, the electrodes are often made from zinc and manganese oxide. These electrodes are separated by the electrolyte - usually in the form of a paste or a liquid. When the battery is wired up in a circuit, an electrochemical reaction takes place. Positively charged ions move from one electrode to the other through the electrolyte. Negatively charged electrons flow from one electrode, out of the battery, out through the circuit, and back to the other electrode. It's this flow of electrons that transfers electrical energy to where it is needed.
Alkaline batteries, like this, eventually run out of stored energy. They can be recycled, but need to be replaced. Rechargeable batteries, like the battery in a phone, can be used again and again. Rechargeable batteries can hold more energy than alkaline batteries. Some can hold huge amounts.
Here in Scotland, at the Whitelee Wind Farm they are introducing a fifty megawatt super battery which is larger than a tennis court. When the wind farm generates more electricity than is being used, some of it can be used to charge this massive battery. When the wind isn't blowing, the battery can be used to keep the electricity supply topped up.Batteries have allowed us to be more mobile and have changed the way we have worked, travelled, and communicated for decades. But there are some pretty big drawbacks. Compared to mains electricity, batteries are more expensive, and they store a small amount of energy.
Dr. George Loumakis, Lecturer in energy:Lithium is used a lot in many mainstream batteries. Whenever we think about every day batteries, like the ones we use in our phones, we use lithium. Lithium is definitely not a renewable. A renewable, by definition, is something that has the ability to renew itself. So, if we're talking about materials, it should be an organic material that has the ability to replenish itself. It is widely used a lot in the electronics industry because it has very good capabilities. The problem is that mining lithium is very environmentally harmful. When it is time to dispose of lithium, disposal is problematic and contains hazardous materials and hazardous products and processes.
Rechargeable batteries require lots of lithium. There is only a certain amount of lithium in the world. So, we rely on batteries every day, and they can play a big part in making renewable energies work more reliably, but does this out-weigh their environmental costs?
What is a battery?
Usually a battery is made up of cells. The cell is what converts the chemical energy into electrical energy.
A simple cell contains two different metals (electrodes) separated by a liquid or paste called an electrolyte. When the metals are connected by wires an electrical circuit is completed.
One metal is more reactive than the other. Negatively-charged electrons flow from the more reactive metal through the wires to the less reactive metal. In the graphic above, electrons flow from the magnesium to the copper. Positively-charged ions flow from the copper through the electrolyte to the magnesium.
Electricity will continue to flow until there is no more magnesium left to react.
How batteries work
Batteries are stores of chemical energy. When being used in portable electrical devices like your phone, they transfer chemical energy into electrical energy.
When a battery stops working, it is because the chemicals in it have been used up. Some batteries are rechargeable and when they are being recharged, electrical energy (from the mains) is transferred back to chemical energy (in the battery) to be used again.
Case study: lemon cells
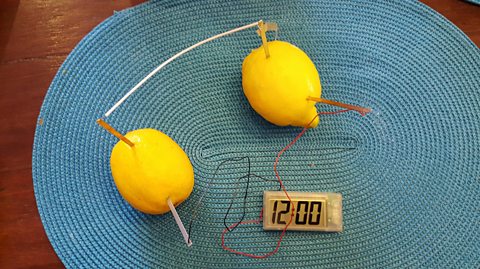
You could make your own lemon battery. Put a copper penny (one and two pence pieces work) into the lemon, this will form the positive electrode, and a galvanized zinc nail for the negative electrode.
These can then be attached to a light bulb or buzzer using alligator clips and wires. Three or four lemons are likely to be required to light the bulb. This experiment can be used to explain how a battery works. A battery requires three things – two electrodes and an electrolyte.
The electrodes must be different materials with different chemical reactivity to allow electrons to move round the circuit. This movement requires an electrolyte to complete the circuit, provided by the acidic liquid in the lemon. The flow of electricity can be measured using a voltmeter.
Creating different voltages
Different metals produce different voltages in a cell. You can list the different metals in order of the size of the voltage that is made when connected to the same metal. This list is called the electrochemical series. This list is very important for chemists and people who are interested in the reactions of metals.
Other factors affect the size of voltage produced in a cell such as:
- the type of electrolyte.
- the concentration of electrolyte.
- the distance between electrodes.
- the surface area of the electrodes.
Sustainability
To develop a sustainable future you need to think about meeting today's needs and protecting the environment and resources for the future.
Although very useful, batteries are not a renewable source of energy. They are made from non-renewable materials such as lithium (used to make rechargeable batteries).
Batteries can also be difficult to recycle as they contain toxic substances.
There is work being done to try and make batteries more sustainable. Scientists are trying to make batteries out of chemicals such as sodium that are more common and more sustainable.

Advantages and disadvantages of batteries
Advantages
- They are portable and have changed how we live and work.
- Some batteries are a clean method of generating electricity for transport as they do not produce carbon dioxide.
- Batteries are used to store electricity that is surplus to requirements. This means that energy is not being wasted.
Disadvantages
- They are expensive to use.
- They (usually) store only a small amount of energy.
- They contain finite resources such as precious metals. This is why it is essential that we recycle batteries.
- Mining precious metals and making batteries produce toxic waste which is dangerous to the environment.
- They can leak corrosive chemicals (from the electrolyte).
Test your knowledge
More on Energy sources and sustainability
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 12

- count3 of 12

- count4 of 12

- count5 of 12
