Introduction to electromagnetism
Key points
An electromagnet uses an electrical current to generate a magnetic field.
There are three ways to strengthen an electromagnet:
increasing current
increasing the number of turns of the coil
adding an iron core
An electromagnet with a permanent magnet can be used to make motors and loudspeakers.
Game - electromagnets
Play an Atomic Labs experiment exploring electromagnets.
You can also play the full game
Electromagnetism
A video about electromagnetism
A video that shows how electromagnets work
Magnets like this one are great at picking up metal objects like these, but once you pick them up how do you let them go?
For that you need a special type of magnet – an electromagnet.
Magnetism and electricity are very closely related. If a magnet is moving near to a wire it will generate an electric current and if an electric current is moving through a metal it can make a magnetic field. This is called an electromagnet.
If you turn off the electric current, the magnetic field will disappear and the magnetism will stop.
Which means we have a magnet that can be switched on or off.
Let’s find out more about how an electromagnet works.
When an electric current, like the one generated by a power pack, flows through copper wire it creates a magnetic field and we have made… an electromagnet. Because iron is a magnetic material, adding an iron core makes the magnetic field stronger.
But this electromagnet is still quite weak, see? It’s only holding onto one of our paperclips.
But if I coil the wire more times around the iron then I am wrapping the same electric current round and round the iron core, building up the magnetic field and making the electromagnet stronger.
When the power is on, the electromagnet attracts magnetic metals.
And when the power is off, the magnetic field disappears, and the metals drop, just like in the recycling centre!
The relationship between electricity and magnetism is so important for lots of kinds technology:
- it helps wind turbines generate electricity
- it makes motors like the ones in food processors spin
- and it helps microphones and loudspeakers work.
Right! Any requests?
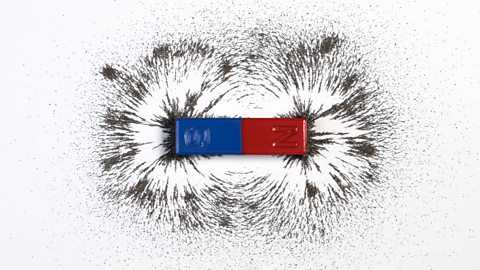
Any wire with current flowing through it has a magnetic fieldThe area around a magnet where a force may be felt.. Most of the time the magnetic field is too small to be important or have any noticeable effect.
The magnetic field lines around a current-carrying wire are circular. The field lines are closer together near the wire. This shows that the magnetic field is stronger when close to the wire.
A coil of wire with many turns is called a solenoidA coil of wire with many turns..
The shape of the magnetic field around a current-carrying solenoid is like the magnetic field pattern of a bar magnet.
If the magnetic field becomes strong enough to be useful, it is called an electromagnet.
A typical electromagnet consists of a wire coiled around an iron core.
The iron core is often called a soft iron core. This is because iron is magnetically soft. This means the iron core is easy to magnetise and easy to demagnetise.

Electromagnets are used in automatic door locks, headphones, scrap yard cranes and even to make magnetic, levitating trains.


Electromagnets can be switched on and off. They are only magnets while current is flowing though the coil. Electromagnets can be made stronger or weaker.

Increasing the strength of the electromagnet
There are three main ways to increase the strength of an electromagnetA magnet formed by an electrical current. An electromagnet can be switched on and off..
- Using more turns on the coil of wire will produce a stronger magnetic field.
Coiling up a longer piece of wire adds up the magnetic field of each turn.
- A greater current will produce a stronger magnetic field.
- Adding a soft iron coreA piece of iron that is placed inside a solenoid. It is used to increase the strength of an electromagnet. increases the strength of an electromagnet.
Iron is a magnetic material. A coil of wire is wrapped around an iron core. The iron core becomes magnetised when the electromagnet is switched on. This increases the overall strength of the electromagnet.
Try the experiment online
Try out this experiment in Atomic Labs. Go to the Physics lab and try the Electromagnets experiment.
Atomic Labs game. gameAtomic Labs game
Try out practical experiments in this KS3 science game

The motor effect
If two of the same polesThe ends of a magnet, where the magnetic field is strongest. Poles can be north or south. (either north with north or south with south) are brought near each other, they push each other away. Like poles repel.
If two opposite poles (north with south) are brought near to each other, they pull towards each other. Un-like poles attractionWhen forces pull objects towards each other. The objects attract each other..
Find out more about magnetism in the Magnets and magnetic fields guide.
Knowing that two magnets can attractionWhen forces pull objects towards each other. The objects attract each other. or repulsionWhen forces push objects away from each other. The objects repel each other. helps us to explain how an electric motor works. In the diagram, Both the permanent magnet and the current-carrying wire have a magnetic field around them. The permanent magnet and the wire exert a force on each other.
The force on a current-carrying wire near a permanent magnet causes the wire to move. This effect is called the motor effect. This is used in a DC motor.
1. Looking at the diagram of the split ring commutator, what do you think would happen if you reversed the cell?
2. What do you think would happen if you swapped the poles of the magnet?
The motor would spin in the opposite direction.
The motor would spin the opposite direction.
Electromagnets in headphones and loudspeakers

A device supplies an electrical signal to a coil of wire that is attached to a cone. When current flows one way through the coil, the cone is pushed forward. When current flows in the opposite direction, the cone is pulled backwards. As the current in the coil repeatedly changes direction it makes the cone vibrate. The air vibrates and sound waves travel to our ears.

Electromagnets in microphones

Microphones have a very similar structure to speakers. Both have a coil of wire that is able to move near a permanent magnet.
In the microphone however, incoming sound causes the diaphragm to vibrateMove back and forth rapidly.. This moves the attached coil of wire.
The effect is the opposite of the motor effectWhen a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field experiences a force.. The wire moving near the magnet causes an electrical output.

Test your knowledge
Quiz
GCSE exam dates 2025
Find out everything you need to know about the 2025 GCSE exams including dates, timetables and changes to exams to get your revision in shape.

More on Electromagnetism and magnetism
Find out more by working through a topic
- count3 of 4

- count4 of 4

- count1 of 4