Exam practice
GCSE maths: Exam-style quiz by topic
Try this quiz based on GCSE Maths past papers. Choose the topic you would like to revise and answer the questions.
GCSE Maths: exam-style questions
Free interactive maths quizzes based on foundation and higher past papers to help you prepare for your GCSE exams, covering common errors in algebra, graphs.

GCSE Maths: quick-fire questions
Prepare for your GCSE maths higher or foundation exam with this free interactive quiz covering topics including fractions, equations and algebra.

- Guide Number5 Guides
Video playlists
- Video Number3 Videos

- Video Number10 Videos
Quizzes
Quiz: Whole numbers
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying writing whole numbers as words, ordering whole numbers, and multiplying and dividing whole numbers.

Quiz: Whole numbers 2
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying order of operations, negative numbers, adding and subtracting negative numbers.

Quiz: Approximation
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying approximation, rounding to decimal places, rounding to significant figures, truncation, estimating calculations.

Quiz: Decimals
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying place value and ordering decimals, adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing decimals.
Quiz: Multiples and factors
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying multiples and factors, prime, square and cube numbers, powers and roots, and highest common factor.
Quiz: Laws of indices
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying using an index or power, law of indices – multiplication and division, and raising a power to a power.
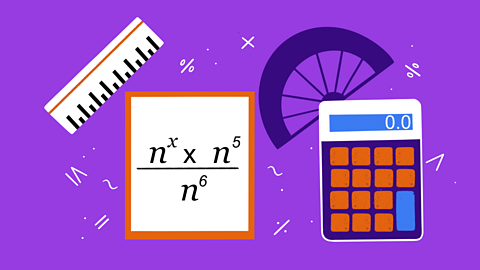
Quiz: Converting between fractions, decimals and percentages
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying converting decimals to fractions and percentages, fractions to decimals, and percentages to decimals.
Quiz: Fractions
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying ordering fractions, using fractions, mixed numbers and improper fractions and fraction arithmetic.
Quiz: Fractions 2
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying ordering and using fractions, multiplying and dividing fractions, fraction arithmetic, and fractions of amounts.
Quiz: Standard form
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying standard form, converting from standard form, ordering numbers in standard form, and calculating standard form.
Quiz: Surds
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying simplifying surds, adding and subtracting surds and rationalising denominators.

Quiz: Financial mathematics
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying wages and salaries, salary and pay, profit and loss, bank statements and savings and VAT.
Quiz: Algebraic expressions
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying expressions, simplifying expressions, expanding brackets, expanding double brackets and expanding three brackets.
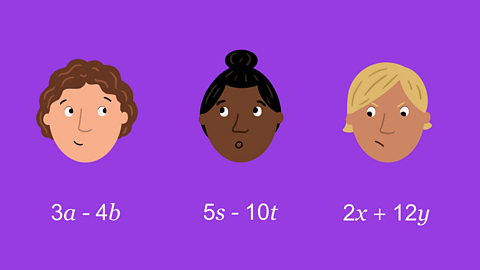
Quiz: Algebraic expressions 2
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying factorising, using algebra to demonstrate an argument, and proof.
Quiz: Algebraic formulae
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying formulae, substitution, creating formulae, changing the subject of a formula, rearranging formulae.
Quiz: Solving linear equations
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying equations and identities, number machines, and solving equations.
Quiz: Solving simultaneous equations
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying simultaneous equations, and solving simultaneous examples with no common coefficients.
Quiz: Solving quadratic equations
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying solving quadratic equations by completing the square, and quadratic functions.
Quiz: Solving quadratic equations 2
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying finding roots by factorising, finding the turning point and the line of symmetry.
Quiz: Inequalities
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying inequalities, solving inequalities, integer solutions to inequalities and graphs of inequalities.

Quiz: Sequences
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying using the nth term, finding the nth term of quadratic sequences, geometric sequences, and special sequences.

Quiz: Straight line graphs
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying coordinates, straight line graphs, parallel and perpendicular lines and equations of a line through two points.
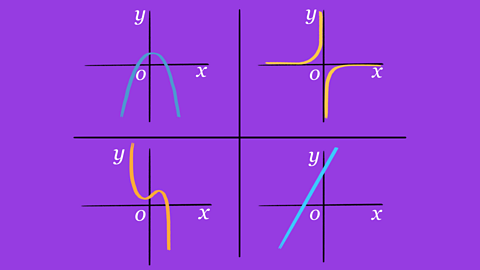
Quiz: Other graphs
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying quadratic graphs, cubic graphs, reciprocal graphs, exponential graphs.
Quiz: Transformation of curves – Higher
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying translating graphs and reflections of graphs.
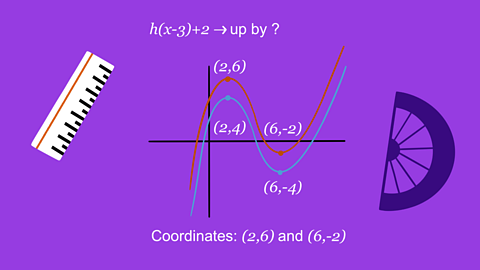
Quiz: Algebraic fractions
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying simplifying rational expressions, factorising, and adding and subtracting rational expressions.
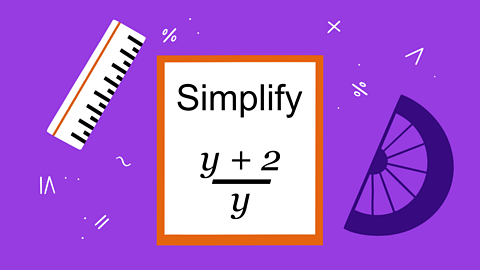
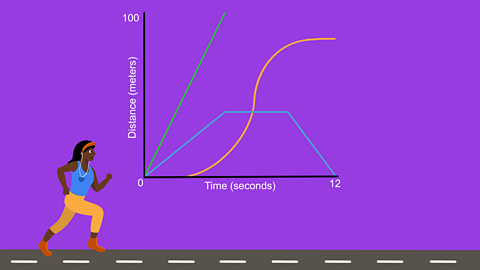
Quiz: Using and interpreting graphs
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE maths students studying real-life graphs, distance-time and displacement-time graphs, speed-time and velocity-time graphs.
Number
NEW: Whole numbers
Use place value to compare and order whole numbers. Practise adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing whole numbers with quizzes and interactive activities.

NEW: Order of operations and negative numbers
Revise how to add, subtract, multiply and divide negative numbers using the correct order of operations (BIDMAS). This guide contains video and quizzes.

NEW: Decimals
Decimal points separate whole numbers from parts of a number. Practise using decimals with video, quizzes and interactive activities.

NEW: Converting between fractions, decimals and percentages
Converting between fractions, decimals and percentages is a useful problem-solving skill. Practise writing data in different formats with quizzes and interactive activities.

NEW: Higher – How to convert recurring decimals
A recurring decimal exists when digits repeat forever. Practise understanding dot notation in recurring decimals with a video, quizzes and interactive activities.

NEW: How to round numbers
Round numbers when an exact value is not needed. Practise rounding to decimal places, estimating calculations and truncation with a video, quizzes and interactive activities.

NEW: What is accuracy in maths?
Limits of accuracy give a range of values a rounded number could have. Practise recognising degrees of accuracy and upper and lower bounds with quizzes and a video for Higher.

NEW: What are fractions?
Fractions show parts of a whole. Learn how to simplify and order fractions, and to write mixed numbers and improper fractions, with quizzes and interactive activities.

NEW: How to add, subtract, multiply and divide fractions
Learn how to add, subtract, multiply and divide fractions, as well as how to use a calculator for fractions and finding fractions of amounts, with video and quizzes.

NEW: Multiples and factors
Revise multiples and factors, prime, square and cube numbers, the product of prime factors and powers and roots, with quizzes and interactive activities.

NEW: Highest Common Factor and Lowest Common Multiple
Revise Highest Common Factor and Lowest Common Multiple, HCF and LCM using prime factors, and powers and roots, with quizzes and interactive activities.

NEW: Laws of indices
Index notation involves a base number (or variable) raised to a power. Practise multiplying and dividing indices, and raising a power to a power, with video and quizzes.

NEW: Negative and fractional indices
Indices may be positive or negative integers, or fractional values. Revise working with negative and fractional indices, with video and interactive activities.
NEW: Standard form
Standard form is a way to write very large and very small numbers so they're easier to work with. Practise working with standard form, with quizzes and interactive activities.

NEW: Calculations using standard form
Learn how to add, subtract, multiply and divide standard form with and without a calculator. Practise writing numbers in standard form with quizzes and interactive activities.

Whole numbers - Eduqas
Numbers can be written in words. Both positive and negative numbers can be added, subtracted, multiplied and divided using rules. These rules must be applied in a specific order.
Approximation - Eduqas
Approximation includes estimation, rounding to powers of 10, decimal places and significant figures.
Decimals - Eduqas
Decimals are used every day, for example, when using money. Knowing how to use decimal points and places when adding, subtracting, dividing and multiplying is an important mathematical skill.

Multiples and factors - Eduqas
Prime numbers, factors and multiples are essential building blocks for a lot of number work. Knowledge of how to use these numbers will improve arithmetic and make calculations more efficient.

Standard form - Eduqas
Calculations with very big or small numbers can be made easier by converting numbers in and out of standard form.

Laws of indices - Eduqas
Using indices, we can show a number times itself many times or as another way of writing a square or cube root. Indices make complex calculations that involve powers easier.

Fractions - Eduqas
Fractions are used commonly in everyday life, eg sale prices at 1/3 off, or recipes using 1/2 a tablespoon of an ingredient. Knowing how to use fractions is an important mathematical skill.

Converting between fractions, decimals and percentages - Eduqas
Fractions, decimals and percentages are frequently used in everyday life. Knowing how to convert between them improves general number work and problem solving skills.

Surds - Higher - Eduqas
Surds are numbers left in square root form that are used when detailed accuracy is required in a calculation. They are numbers which, when written in decimal form, would go on forever.

Financial mathematics - Eduqas
Financial maths is needed for all jobs, from calculating wages to working out profit, loss and VAT. Knowledge of financial maths is also required to be able to understand bank statements and savings.

Algebra
NEW: How to simplify expressions and expand brackets
Revise collecting like terms, using algebraic notation correctly, simplifying expressions, and multiplying a single term over a bracket. This guide contains video and quizzes.
NEW: Factorising expressions
Revise factorising expressions into one or two brackets. For Higher tier, factorise quadratics when the coefficient of 𝑥 squared doesn't equal 1. This guide has video and quizzes.

NEW: Algebraic reasoning and proof
Revise how to use algebra to support and construct arguments, show that two expressions are equivalent, and how to find a counterexample. This guide contains video and quizzes.
NEW: Formulae
Revise writing formulae, substituting into expressions and formulae, and how to change the subject of a formula using inverse operations. This guide contains video and quizzes.

NEW: Higher – Functions
Learn about function notation, how to find an inverse function by changing the subject, and how to work with composite functions. This guide contains a quiz.
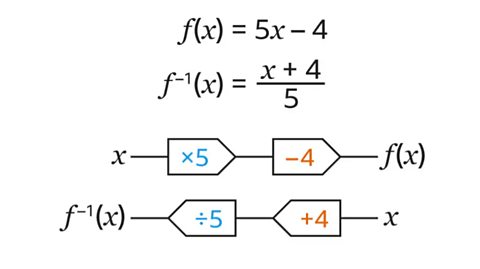
NEW: Solving one- and two-step linear equations
Learn how to use inverse operations to find the value of an unknown variable in an equation, so that the value is true. This guide contains a quiz.

NEW: Solving more complex linear equations
Learn how to solve equations with brackets, 𝑥 terms on both sides, and fractions using inverse operations in this GCSE maths study guide. This guide contains videos and quizzes.

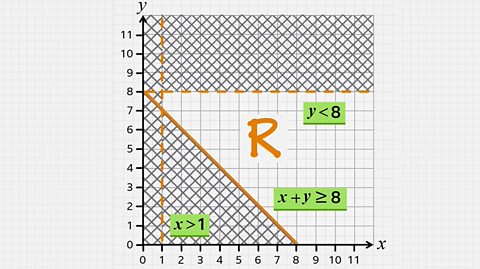
NEW: Inequalities
Inequalities are the relationships between two expressions not equal to one another. The symbols used for inequalities are <, >, ≤, ≥ and ≠. This guide contains video and quizzes.
NEW: Higher – Graphs of inequalities
Revise representing an inequality as a region on one side of a line. Dashed lines on graphs show the line is not included in the region. This guide contains video and quizzes.
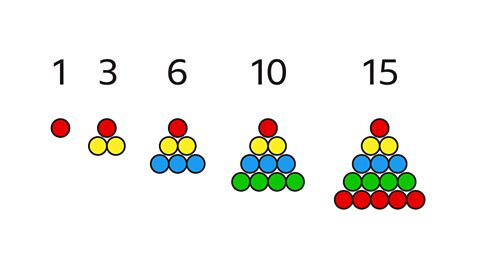
NEW: Sequences
Learn about term-to-term rules, 𝑛th term rules and how to work out expressions for 𝑛th terms based on a set of numbers in a quadratic sequence. This guide contains quizzes.

NEW: Geometric and special sequences
In geometric sequences, the term-to-term rule is to multiply or divide by the same value. Other sequences include square numbers and Fibonacci sequences. This guide has quizzes.
NEW: How to plot straight line graphs
Revise plotting coordinates and creating straight line graphs to show the relationship between two variables. This guide contains video and quizzes.
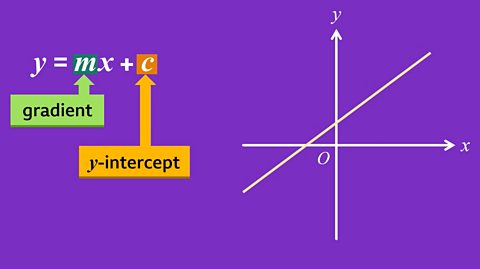
NEW: Working out equations of a line and calculating gradient
Learn how to calculate the equation of a line from a graph, work out the gradient from an equation, and visualise intercepts. This guide contains video and quizzes.
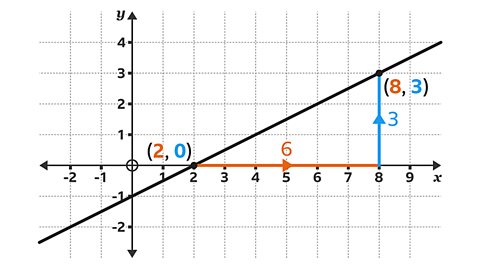
NEW: Equations of parallel and perpendicular lines
Revise finding equations of parallel lines and the gradient of perpendicular lines, and prove that given lines are parallel or perpendicular. This guide contains video and quizzes.
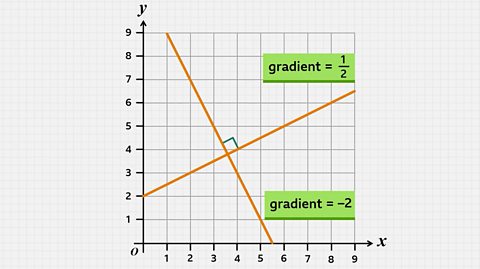
Algebraic expressions - Eduqas
Letters can be used to stand for unknown values or values that can change. Formulas can be written and equations solved to find solutions to a range of problems in science and engineering.
Solving linear equations - Eduqas
Forming, using and solving equations are skills needed in many different situations. From balancing accounts to making sense of a mobile phone bill, solving equations is a vital skill.
Solving simultaneous equations - Eduqas
Simultaneous equations require algebraic skills to find the values of letters within two or more equations. They are called simultaneous equations because the equations are solved at the same time.
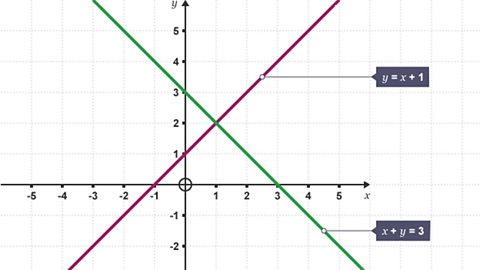
Solving quadratic equations - Eduqas
Solve quadratic equations by factorising, using formulae and completing the square. Each method also provides information about the corresponding quadratic graph.
Algebraic formulae - Eduqas
Formulae are used in everyday life, from working out areas and volumes of shapes to converting units of measurement. Knowing how to use and rearrange formulae are very useful skills.

Inequalities - Eduqas
Inequalities show the relationship between two expressions that are not equal to one another. Inequalities are useful when projecting profits and breakeven figures.

Sequences - Eduqas
Sequences can be linear, quadratic or practical and based on real-life situations. Finding general rules helps find terms in sequences.

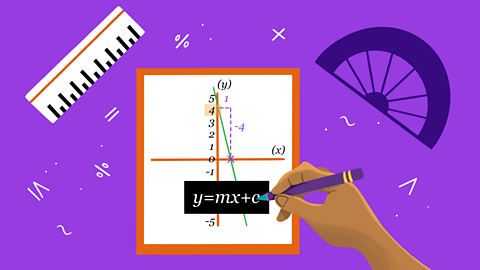
Straight line graphs - Eduqas
y = mx + c is an important real-life equation. The gradient, m, represents rate of change (eg, cost per concert ticket) and the y-intercept, c, represents a starting value (eg, an admin. fee).

Other Graphs - Eduqas
The most commonly occurring graphs are quadratic, cubic, reciprocal, exponential and circle graphs. Their equations can be used to plot their shape.
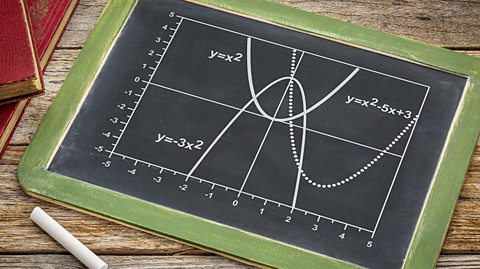
Transformation of curves - Higher - Eduqas
Functions of graphs can be transformed to show shifts and reflections. Graphic designers and 3D modellers use transformations of graphs to design objects and images.
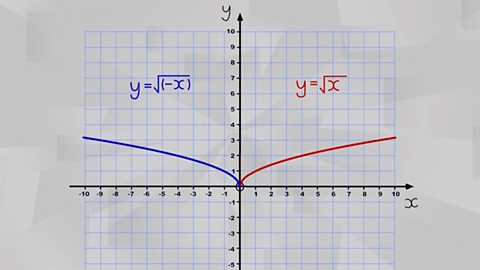
Using and interpreting graphs - Eduqas
Using graphs is not just about reading off values. In real-life contexts, the intercept, gradient and area underneath the graph can have important meanings such as a fixed charge, speed or distance.

Algebraic fractions - Eduqas
Algebraic expressions in fraction form are rational. Methods of adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing fractions plus expanding and factorising can be used to simplify rational expressions.
Ratio, proportion and rates of change
Ratio in context - Eduqas
Ratios are seen in everyday life. They can be used when adding ingredients to make a meal, when deciding how much pocket money children get or when reading a map.

Percentages - Eduqas
Percentages are used in everyday life, for example, calculating discounts during sales and interest rates at banks. Knowing how to find and use percentages is an important skill.

Direct and inverse proportion - Eduqas
Proportion is used to show how quantities and amounts are related to each other. The amount that quantities change in relation to each other is governed by proportion rules.
Geometry and measure
Angles, lines and polygons - Eduqas
Polygons are multi-sided shapes with different properties. Shapes have symmetrical properties and some can tessellate.

Loci and constructions - Eduqas
Loci are a set of points with the same property. Loci can be used to accurately construct lines and shapes. Bearings are three figure angles measured clockwise from North.

2-dimensional shapes - Eduqas
2-dimensional shapes are flat. The perimeter of a 2D shape is the total distance around the outside of the shape. The area of a 2D shape is the space inside the shape.

3-dimensional shapes - Eduqas
3-dimensional shapes have faces, edges and vertices. Volume is the space contained within a 3D shape. Surface area is the sum of the area of each face. 3D shapes can be viewed from different points.
Circles, sectors and arcs - Eduqas
Circles are 2D shapes with one side and no corners. The circumference is always the same distance from the centre - the radius. Sectors, segments, arcs and chords are different parts of a circle.

Circle theorems - Higher - Eduqas
Circles have different angle properties described by different circle theorems. Circle theorems are used in geometric proofs and to calculate angles.

Transformations - Eduqas
Transformations change the size or position of shapes. Congruent shapes are identical, but may be reflected, rotated or translated. Scale factors can increase or decrease the size of a shape.

Pythagoras' theorem - Eduqas
Pythagoras’ theorem can be used to calculate the length of any side in a right-angled triangle. Pythagoras’ theorem can be applied to solve 3-dimensional problems.

Units of measure - Eduqas
A unit of measurement describes one unit of a quantity. Units of measurement can be imperial or metric. They can be converted using conversion factors.

Trigonometry - Eduqas
The three trigonometric ratios; sine, cosine and tangent are used to calculate angles and lengths in right-angled triangles. The sine and cosine rules calculate lengths and angles in any triangle.

Vectors - Eduqas
A vector quantity has both size and direction. Vectors can be added, subtracted and multiplied by a scalar. Geometrical problems can be solved using vectors.

Probability
Probability - Eduqas
Probabilities can be written as fractions, decimals or percentages on a scale from 0 to 1. Knowing basic facts about equally likely outcomes can help to solve more complicated problems.

Statistics
Collecting data - Eduqas
Many companies and organisations collect data to improve their information and products. Skills in collecting data can make this process more efficient and reliable.

Representing data - Eduqas
Data is represented in many different forms. Using bar charts, pie charts and frequency diagrams can make information easier to digest.
Analysing data - Eduqas
An average is the typical value within a set of data. There are three forms of average: mean, median and mode. It is important to know what they are and which form of average to choose.

Problem solving
Problem solving introduction - Eduqas
Mathematical problems cover many different areas of Maths. A framework can be applied to help identify the information needed to solve the problem and to check the answer.
Solving 'number' problems - Eduqas
Number problems often involve a combination of fractions, decimals, percentages and ratio. They can be set in a real-life context. A framework can be used to tackle these problems.

Solving 'graphical' problems - Eduqas
Graphical problems will usually be linked to a real-life situation. Travel graphs, temperature graphs and conversion graphs are common graphs. A framework can be used to tackle graphical problems.
Solving 'geometric' problems - Eduqas
Geometric problems can involve finding the perimeter and area of shapes like triangles and quadrilaterals. Knowledge of shape properties is essential. A framework can be used to tackle these problems.

Solving 'algebraic' problems - Eduqas
Algebra problems can relate to any area of maths. Problems often include a mix of algebra, number and geometry. A framework can be used to tackle these problems.

Solving 'statistical' problems - Eduqas
Number problems often involve a combination of fractions, decimals, percentages and ratio. They can be set in a real-life context. A framework can be used to tackle these problems.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link