Watch: What is a biodiversity investigation?
What are the key terms in fieldwork and competition?
Biodiversity: a measure of the number of different species living in an area.
Population: the number of organisms of the same species living in an area.
Habitat: where a population lives.
Environment: an organism’s surroundings. It contains factors that influence the organism. These factors can be divided into abiotic and biotic factors.
abioticPhysical rather than biological; not derived from living organisms. non-living factors eg temperature.
BioticLiving or once living components of a community; for example organisms, such as animals and plants.: living factors eg a predator.
Community: several populations of different species living in habitats close together.
Ecosystem: an area where a community of organisms live and are affected by a range of environmental factors.
What is sampling?

The distribution of organisms in a habitat can be affected by abiotic factors such as temperature and light.
Counting all organisms in a large area is often difficult due to time limits and because animals may hide.
To address this, small sections within the larger area are sampled.

Effective sampling should be:
reliable, a large sample size is needed – 20 to 30 quadrats counted.
representative of the habitat being investigated. Quadrats should be placed randomly to produce valid results and avoid bias.
What are quadrats?
Quadrats are a small square frame that can be used to investigate the abundance of plants and non-motileAnimals that lack the ability to move from one place to another independently, and are typically permanently attached to a substrate. animals in a habitat.

Practical - How do you use quadrats to investigate a habitat?
Quadrat - random sampling
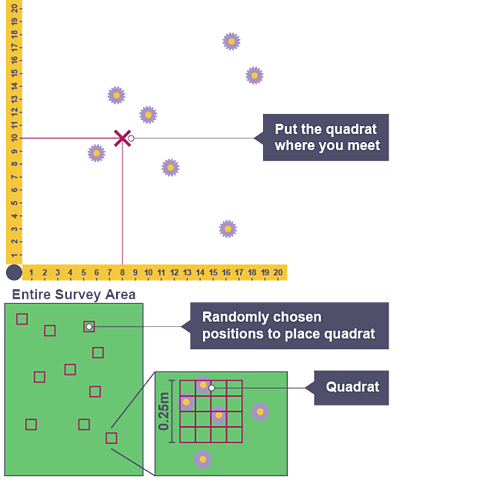
Procedure
- Place two measuring tapes at right angles to create a co-ordinate grid.
- Use a random number generator to make random coordinates.
- Place a quadrat at each coordinate.
- Count the numbers of each species in each quadrat.
- Use a key to identify unknown species.
- Record results in a table.
- Calculate the average of each species per quadrat.
- Multiply the average by the total area to estimate the population size of each species in the habitat.
Quadrat - belt transect
The belt transect is used to study changes across a habitat.
Procedure
- Place a measuring tape (10m) across the habitat.
- Place a quadrat at regular intervals (eg every 1 m) along the transect line.
- Count the numbers of each species.
- Record results in a table.
- Repeat step 2-4 to get reliable results.
- Calculate the average number of each species at each interval.
- Plot results on a bar graph.
Results
| Distance from shoreline (m) | Sea lettuce | Barnacles | Sea anemones |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 0 |
| 1 | 8 | 12 | 1 |
| 2 | 6 | 9 | 3 |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 11 |
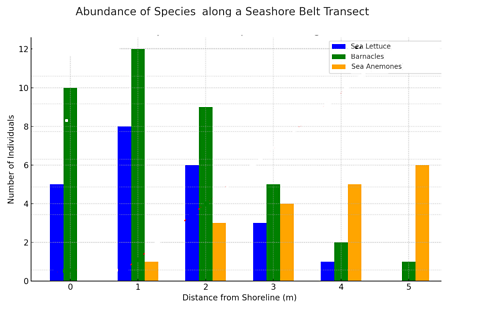
Conclusion:
The number of sea lettuce and barnacles decrease with increasing distance from the shoreline whereas the number of sea anemones increase because there are different conditions at various distances from the shore.
Environmental factors
An organism’s surroundings (abiotic and biotic factors) can influence its distribution.
Abiotic (non-living) factors

Image caption, Wind speed is measured with an anemometer. It affects the rate of water loss by plants and therefore affects their survival rates in exposed areas.

Image caption, Water levels in soil are measured by finding the mass of a soil sample, drying the sample in an oven and reweighing. The difference in mass gives an indication of the percentage soil moisture. It affects the survival and therefore distribution of plants and animals.

Image caption, pH levels are measured using a pH probe. It affects the survival and therefore distribution of plants. Most plants prefer neutral conditions but some will only grow in acidic or alkaline conditions

Image caption, Light is measured using a light meter. All plants need light to photosynthesise. It affects the survival and therefore distribution of plants.

Image caption, Temperature is measured with a thermometer. It affects the rate of cell reactions like photosynthesis.
1 of 5
Biotic (living) factors
Biodiversity is measured by using quadrats and belt transects.
Other plants and animals can affect the distribution of an organism.
Biotic factors, like predation and competition, strongly influence species distribution. For example, high predator numbers can reduce prey populations, while limited food resources can heighten competition and impact survival.
Biotic factors are much more difficult to measure than abiotic.
What is competition in the natural world?
Competition between animals is usually for:
- food
- water
- territory
- mates
Competition between plants is usually for:
- light
- water
- minerals
- space
Competition for these resources can affect population growth.
Organisms have adapted to their individual environments and to any competition for resources.
Human effect on the ecosystem
Humans can also influence the normal balance of an ecosystemA community of animals, plants and microorganisms, together with the habitat where they live..
Humans disrupt ecosystem balance through activities such as:
- deforestation
- pollution
- overfishing
- climate change
These actions alter habitats, reduce biodiversity and destabilise food webs, impacting the health and endangering species.
Competition affecting organism populations
Red and grey squirrels
The grey squirrel is not native to the UK - it was introduced from North America.

There is great competition between the red and grey squirrel with the population of the grey outweighing that of the red in some areas.
This has happened for a number of reasons.
The grey squirrel eats a wider range of food and can survive in areas of mixed woodland whilst the red squirrel cannot.
The grey squirrel carries a disease that is fatal to red squirrels while the grey remains unaffected.

However, grey squirrels are much larger than red squirrels and need more food to survive.
In areas where seeds are small (eg conifer forests) the grey squirrel struggles to obtain enough food and the red squirrel dominates.
Watch: Classification of organisms
Test your knowledge
More on Biodiversity
Find out more by working through a topic
- count2 of 5

- count3 of 5
