Key points
- Ferrous metals contain iron, are strong and magnetic, and are used in construction, car manufacturing, and machinery parts.
- Non-ferrous metals do not contain iron, are resistant to rust, and are used in aerospace, construction, and packaging.
- Alloys are mixtures of metals designed to enhance properties like strength and durability, used in construction, cars, and tools.
- Graphene is incredibly strong, lightweight, and conducts electricity and heat, used in electronics and materials strengthening.
- Graphene's properties include excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for electronic devices and water purification.
Properties and applications of ferrous and non ferrous metal
What are ferrous metals?
Ferrous metals contain iron and are strong and magnetic. They are used in many different things because they are durable and can be shaped into various forms. They can rust if not protected but are important in many industries.
| Properties | Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | Mild steel is Ductileable to be drawn out into a thin wire, not brittle and malleableCapable of being hammered or pressed into a new shape without breaking., easily shaped and welded. It has good tensile strength and impact resistance, commonly used in structural applications but requires protective coatings to prevent rusting. | Mild steel is widely used in construction, car and manufacturing industries. It is found in structural steelwork, pipes, steel frames, metal furniture and machinery parts. |
| Carbon steels | Carbon steels are classified as low medium or high carbon steels. Low carbon steels are ductile medium carbon steels balance strength and ductility while high carbon steels offer hardness and wear resistance. | Carbon steels are used in a wide range of applications Low Carbon Steel Structural beams, pipes and car bodies. Medium Carbon Steel Gears, crankshafts, machinery parts. High Carbon Steel Cutting tools, blades, springs. |
| Stainless Steel | Stainless steel is durable rust and corrosion resistant with a silvery metallic finish. It has high tensile strength and ductility, making it popular for architectural and kitchen applications with a clean appearance. | Kitchenware Cutlery, pots and pans, appliances. Construction Structural supports and handrails. Medical Equipment Surgical instruments, implants, hospital equipment. |

Image caption, Mild steel is strong but easily shaped and is used in construction

Image caption, Medium carbon steel is stronger than mild steel making it excellent for tools

Image caption, Stainless steel is used in cooking implements due to its corrosion resistance
1 of 3
What are non ferrous metals?
Non ferrous metals do not contain iron and are resistant to rust. They are often lighter and have different properties compared to ferrous metals.
| Properties | Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminium | Aluminium is lightweight malleable and ductile allowing easy shaping. It conducts heat and electricity well. Its high strength to weight ratio makes it corrosion resistant but has lower tensile strength under heavy stress. | Aerospace Aircraft frames Construction Window frames, roofing, cladding. Transportation Car parts, bicycles, trains. Packaging Foil, cans, containers. |
| Brass (alloy of copper and zinc) | Brass has a golden yellow colour resembling gold. It is strong corrosion resistant and easily machinable. Its shiny appearance makes it popular for decorative items, jewellery and musical instruments. | Plumbing Fittings Valves and pipe fittings. Decorative Items Ornaments, jewellery. Musical Instruments Trumpets, trombones, saxophones. Engineering Components Gears, bearings, locks. |
| Copper | Copper is soft malleable and ductile with reddish brown colour and high thermal and electrical conductivity. It resists corrosion but develops a green layer over time. It is essential for electrical wiring. | Copper is used in Electrical Wiring Cables, electrical contacts, circuit boards. Plumbing Pipes, fittings and fixtures. Construction Roofing, gutters, architectural details. |

Image caption, Aluminium is lightweight and ductile making it useful in food packaging

Image caption, Brass combines copper and zinc to improve properties like strength or conductivity

Image caption, Copper's resistance to corrosion means it can be used as water pipes
1 of 3
What are alloys?
Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals or a metal and another element, combined to enhance certain properties. They are designed to improve strength, durability or other characteristics compared to the individual metals alone. For example, alloys can be stronger, more resistant to corrosion or more flexible.
Key properties of alloys
Enhanced Strength
Alloys are often stronger than their original metals. For example, steel (an alloy of iron and carbon) is much stronger than pure iron.
Improved Durability
Many alloys are more resistant to wear and tear. For instance, stainless steel is resistant to rust and corrosion.
Specific Properties
Alloys can be engineered to have specific properties such as hardness, flexibility or resistance to extreme temperatures.
Alloys are crucial in many industries due to their ability to combine different metal properties to meet specific needs and enhance overall performance.
Common alloys and their uses
| Alloy | Properties | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Steel (Iron and Carbon) | Strong and versatile. Can be hardened or tempered | Construction, car, tools |
| Stainless Steel (Iron, Chromium, Nickel) | Corrosion resistant and durable | Kitchenware, medical instruments, structural applications |
| Brass (Copper and Zinc) | Malleable, good acoustic properties, resistant to corrosion | Musical instruments, plumbing fittings, jewellery |
What is graphene?
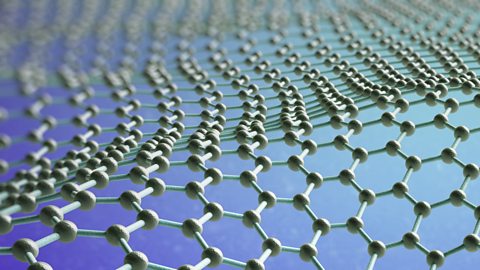
Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal pattern. It is incredibly strong, lightweight and conducts electricity and heat very well.

Facts about graphene
A quick overview of woods, plastics and metals.
Knowing which material to use when designing or manufacturing a product is a very important skill to have. Different materials have a wide range of different properties. This means that choosing the correct material to use is a very important decision in the design and manufacturing process. In this video we will go over the most common material and their properties.
Wood can be split into 3 main categories. Hardwoods, softwoods and manufactured boards.
Hardwoods: These are generally a very hard and tough wood. They also give the best finish. However, they are more difficult to work with and can also be very expensive. Hardwoods come from deciduous trees and therefore take a long time to grow.
Softwoods:These are a much softer type of wood. They are however, much easier to cut and work with. They are also much cheaper than hardwoods. They are not as durable or long-lasting as hardwoods. Softwoods come from coniferous trees. They grow much faster than deciduous trees.
Manufactured Boards: These are man-made materials. Made using a number of different techniques. Each type of board for example plywood or chipboard are produced to have specific properties. They are also the cheapest type of wood to use. Manufactured boards do not give the nicest finish and will not last as long as the other two types.
Plastics are split into two categories, thermoplastics and thermosets.
Thermoplastics can be heated and shaped many times. Examples of thermoplastics are acrylic. This is used to make car headlights. It is often used as a glass alternative. Rigid polystyrene is another example. A common use of this would be for simple toys as it is hard while still being light.
As plastics can be moulded, a much more complex shape can be produced. Thermoset plastics can only be heated and shaped once. They are therefore more commonly found in instances where heat is more an issue. For example light fittings or a saucepan handle.
Metals are most commonly split into 3 categories ferrous, non-ferrous and alloys. Ferrous metals contain iron and therefore easily rust. They are also magnetic. Examples of these are iron and steel.
Non-Ferrous Metals do not contain iron, they therefore don't rust. They are also not magnetic. Some common examples are aluminium and copper. Lastly we have alloys. These are made up of a mixture of more than one metal. The most common examples of these are bronze (copper and tin) and brass (copper and zinc)
Test yourself
More on Manufacturing - materials
Find out more by working through a topic