Key points
- Material characteristics are grouped as physical (e.g., density, conductivity), aesthetic (e.g., colour, texture), and structural (e.g., strength, elasticity).
- Thermosetting plastics set permanently when heated and are used for electrical insulators and car parts (e.g., melamine, epoxy resin).
- Thermoplastics can be melted and reshaped multiple times and are used for containers, toys, and pipes (e.g., acrylic, PVC).
- Hardwoods are strong, durable, attractive, and come from broad-leaved trees; they are used for furniture and flooring (e.g., oak, mahogany).
- Softwoods are lighter and easier to work with than hardwoods and come from coniferous trees; they are used in construction and furniture (e.g., pine, cedar).
- Manufactured boards are made from wood fibres or particles and are consistent and versatile; they are used in furniture and construction (e.g., plywood, MDF, chipboard).
Introduction to Materials
A quick overview of woods, plastics and metals.
Knowing which material to use when designing or manufacturing a product is a very important skill to have. Different materials have a wide range of different properties. This means that choosing the correct material to use is a very important decision in the design and manufacturing process. In this video we will go over the most common material and their properties.
Wood can be split into 3 main categories. Hardwoods, softwoods and manufactured boards.
Hardwoods: These are generally a very hard and tough wood. They also give the best finish. However, they are more difficult to work with and can also be very expensive. Hardwoods come from deciduous trees and therefore take a long time to grow.
Softwoods:These are a much softer type of wood. They are however, much easier to cut and work with. They are also much cheaper than hardwoods. They are not as durable or long-lasting as hardwoods. Softwoods come from coniferous trees. They grow much faster than deciduous trees.
Manufactured Boards: These are man-made materials. Made using a number of different techniques. Each type of board for example plywood or chipboard are produced to have specific properties. They are also the cheapest type of wood to use. Manufactured boards do not give the nicest finish and will not last as long as the other two types.
Plastics are split into two categories, thermoplastics and thermosets.
Thermoplastics can be heated and shaped many times. Examples of thermoplastics are acrylic. This is used to make car headlights. It is often used as a glass alternative. Rigid polystyrene is another example. A common use of this would be for simple toys as it is hard while still being light.
As plastics can be moulded, a much more complex shape can be produced. Thermoset plastics can only be heated and shaped once. They are therefore more commonly found in instances where heat is more an issue. For example light fittings or a saucepan handle.
Metals are most commonly split into 3 categories ferrous, non-ferrous and alloys. Ferrous metals contain iron and therefore easily rust. They are also magnetic. Examples of these are iron and steel.
Non-Ferrous Metals do not contain iron, they therefore don't rust. They are also not magnetic. Some common examples are aluminium and copper. Lastly we have alloys. These are made up of a mixture of more than one metal. The most common examples of these are bronze (copper and tin) and brass (copper and zinc)
Material properties and characteristics can be broken down into three key categories physical, aesthetic and structural characteristics.
These characteristics guide designers and engineers in selecting the right material for a specific application.
Physical characteristics
These refer to the measurable properties of a material, such as density, hardness, thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity.
Density is the amount of mass a material has for a given volume. It shows how heavy or light a material is compared to it's size.
Hardness is a measure of how resistant a material is to being scratched, dented or worn down. It indicates how tough the surface of the material is.
Thermal conductivity is how well a material transfers heat. A material with high thermal conductivity quickly moves heat through it, while one with low thermal conductivity resists heat flow.
Electrical conductivity is a material's ability to allow electric current to pass through it. A material with high electrical conductivity easily lets electricity flow, while one with low conductivity resists it.
Aesthetic characteristics
These describe the materials appearance and how it appeals to the senses. It includes colour, texture and finish.
Colour is the visual characteristic of a material determined by how it reflects or absorbs light. It affects the appearance of the material and can influence the aesthetic appeal and identification.
Texture describes the surface feel and appearance of a material, including whether it is smooth, rough, bumpy or glossy. It affects both how the material looks and how it feels to the touch.
Finish refers to the final surface treatment or coating applied to a material, affecting the appearance and feel. It can be glossy, matt, smooth or textured and influences durability, resistance to wear and overall look.
Structural characteristics
These relate to a material's ability to withstand forces, including strength, toughness, elasticity and stiffness.
Strength is a material's ability to withstand force without breaking or deforming. It indicates how much load a material can handle before it fails.
Toughness is a measure of how well a material can handle being hit or stressed without breaking. It means the material can absorb a lot of force and still stay intact.
Elasticity is a material's ability to return to its original shape after being stretched or compressed. It means that when you apply force, the material can change shape, but once the force is removed, it goes back to how it was before.
Stiffness is a measure of how much a material resists bending or stretching. A stiff material does not change shape easily when force is applied to it. It stays firm and rigid, making it less flexible.
Thermosetting plastics and thermoplastics
Thermosetting plastics
Thermosetting plastics are materials that set hard when heated and cannot be remelted. They are durable, heat resistant and maintain their shape even at high temperatures. Once set, they are rigid and strong, making them ideal for things like electrical insulators and car parts.
| Properties | Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Melamine | Melamine is hard, durable and heat resistant. It has a smooth glossy finish and is suitable for long lasting surfaces. | Household and commercial products where strength, aesthetics and heat resistance are important such as picnic plates cupboard doors and countertops. |
| Polyester Resin | Polyester resin is lightweight rigid and resistant to chemicals. It can be transparent or coloured and becomes durable when reinforced. | Boat hulls and car bodies |
| Epoxy resin | Epoxy resin has high strength durability and chemical resistance. It can be clear or coloured with a glossy smooth finish and is used in resin art furniture and countertops. | Resin art, furniture and countertops |
| Urea Formaldehyde (UF) | Urea formaldehyde is hard, rigid and heat resistant. It has high tensile strength. It is an excellent electrical insulation. | It can be moulded and coloured with a smooth glossy surface for various applications. |

Image caption, Piece of worktop coated with melamine

Image caption, Boat maker putting glass fibres into polyester resin

Image caption, Artist pouring epoxy resin

Image caption, Electrical sockets are often made from urea formaldehyde (UF)
1 of 4
Thermoplastic
Thermoplastics are plastics that can be melted and reshaped multiple times when heated. They are flexible and can be moulded into various shapes, making them useful for items like containers, toys and pipes. Unlike thermosetting plastics, they return to a liquid state when heated and can be reprocessed.
| Properties | Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Acrylic | Acrylic is lightweight strong and shatter-resistant with good weather and UV resistance. It is clear and durable available in various colours with glossy or matt finishes and has good impact resistance. | Acrylic's transparency, durability and weather resistance make it suitable for signs, windows, display cases and aquariums. |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | PVC is lightweight durable and resistant to moisture and chemicals. It can be rigid or flexible, available in various colours and finishes and is used in window frames and flooring | Rigid PVC is often used in construction (windows & drain pipes). Flexible PVC is used in plumbing and electrical cables. |
| ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) | ABS is lightweight rigid and impact resistant. It is tough and resistant to chemicals heat and abrasion. It withstands low temperatures better than other plastics and can be moulded into various shapes for polished products. | A combination of strength, toughness and ease of manufacturing makes ABS ideal for toy manufacture and car parts. |
| Nylon | Nylon is strong lightweight and tough with excellent abrasion resistance. It has a smooth surface can be coloured and is used in textiles gears and bearings for its strength and durability. | Nylon’s versatility, toughness and resistance to wear make it suitable for clothing and mechanical parts. |
| Rigid Polystyrene | Rigid polystyrene is lightweight stiff and a good insulator. It can be brittle with a glossy finish available in various colours and can fracture under impact while having good dimensional stability. | Rigid polystyrene is used in packaging and disposable food containers. |
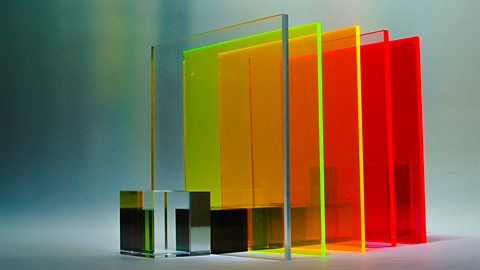
Image caption, Acrylic panels can be both solid colour and transparent

Image caption, Pipes are often made from PVC

Image caption, Toy bricks are made from ABS as it is strong

Image caption, Nylon is often used in mechanical components like gears

Image caption, Rigid polystyrene is lightweight and stiff making it ideal for food containers
1 of 5
Properties and uses of hardwoods, softwoods and manufactured boards.
Hardwoods
Hardwoods come from trees with broad leaves and are known for being strong and durable. They are great for furniture and floors because they can handle heavy use. Hardwoods also have unique grain patterns, which makes them look attractive in various items.
| Properties | Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Mahogany | Mahogany is dense durable and strong, resistant to rot moisture and decay. Its rich reddish brown colour fine grain and excellent dimensional stability make it ideal for outdoor use and finishing. | Mahogany is commonly used for furniture, boat building, musical instruments and veneer due to its combination of strength, beauty and stability. |
| Oak | Oak is dense, heavy and durable with high resistance to wear and impact. Its light to medium brown colour and attractive grain make it ideal for furniture flooring and ageing beautifully. | Oak is commonly used for furniture, flooring, doors, beams and joinery. |
| Beech | Beech is hard, dense and strong with good shock resistance and natural antiseptic qualities. Its pale cream to light brown colour and smooth texture make it ideal for kitchen utensils and finishing. | Beech is widely used for furniture, tool handles, flooring, veneers, kitchen utensils, chopping boards and wooden toys. |

Image caption, Mahogany is dark reddish brown and has a very fine grain

Image caption, A mahogany tree forest in Hawaii

Image caption, Untreated oak is medium brown and has a aesthetically pleasing grain

Image caption, An English oak tree

Image caption, Beech has a slightly pink tint and a smooth texture

Image caption, A green beech woodland
1 of 6
Softwoods
Softwoods come from trees with needles and cones, like pine and cedar. They're usually lighter and easier to cut than hardwoods. Because they grow faster, softwoods are often used in construction and for making things like furniture and paper. They may not be as durable as hardwoods, but they're more affordable and versatile.
| Properties | Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Pine | Pine is lightweight and soft making it easy to work with. It has moderate strength good moisture resistance and a pale yellow or light brown colour, often used in construction for its low cost. | Pine is commonly used in furniture, construction, flooring and doors. It is also popular for DIY projects. |
| Cedar | Cedar is lightweight with good dimensional stability and resistance to warping. Its aromatic scent resists rot and insect damage. Available in light reddish brown to pinkish brown, it's suitable for outdoor uses. | Cedar is commonly used in outdoor furniture, decking, fencing and cladding |

Image caption, Pine is light cream in colour with dark brown lines and knots throughout

Image caption, Pine tree plantation grown for timber

Image caption, The oils in cedar resist insects and make it good for outdoor use

Image caption, Cedar timber plantation in Japan
1 of 4
Manufactured boards
Manufactured boards are made by pressing and gluing together wood fibres or particles. They are consistent and versatile, making them useful for furniture and construction. These boards are often more affordable and adaptable compared to solid wood, offering a practical alternative for various projects.
| Properties | Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Plywood | Plywood is a lightweight, strong material made from glued layers of wood veneerA thin layer of real wood used to enhance the appearance of manufactured board and add strength.. It resists warping and comes in various thicknesses and grades, suitable for both load bearing and decorative applications | Plywood is widely used in construction for walls, roofs, and flooring. It is also used in furniture making, boat building and interior panelling. |
| MDF (Medium Density Fibreboard) | MDF is a dense smooth board with an even texture ideal for detailed machining. It has good dimensional stability and is excellent for painting but can swell and deform when exposed to moisture. | It is also used in doors, drawer fronts and decorative mouldings. |
| Chipboard | Chipboard is lightweight with a uniform texture made from wood particles. It is less dense and weaker than MDF and plywood, often covered with laminate to improve appearance and durability. | Chipboard is commonly used in furniture (especially flat pack furniture), cabinets and packaging. It is also used for shelves, internal partitions and backing for furniture and cabinets. |
| Veneered Manufactured Boards | Veneered boards consist of a core layer like MDF or chipboard covered with a thin veneer of natural wood. This provides a smooth finish mimicking solid wood while adding strength and stability. | Veneered manufactured boards are used in furniture, cabinets, panelling, and doors. |

Image caption, Plywood is made from an odd number of veneer layers which are glued at 90-degree angles for strength

Image caption, Sheets of medium desnsity fiberboard (MDF)

Image caption, Chipboard is commonly covered using a real wood veneer or melamine sheet so it is not on show

Image caption, A veneer is a thin layer of real wood used to enhance the appearance of manufactured board and can add strength. It can be applied to cheaper materials, such as medium-density fibreboard or chipboard, to make them appear more expensive.
1 of 4
Test yourself
More on Manufacturing - materials
Find out more by working through a topic